Deductive Geometry
| Angles | Properties |
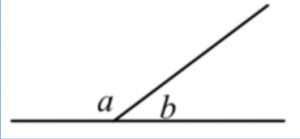 |
a + b = 180°
adj. ∠s on st. line |
 |
a + b + c = 360°
∠s at a pt. |
 |
a = b
vert. opp. ∠s |
 |
a + b + c = 180°
∠ sum of Δ |
 |
a + b = c_1
ext. ∠ of Δ *快捷版,可不記 |
| Properties | Prove | |
| Parallel lines
***見到F/Z/C shape先好用 |
||
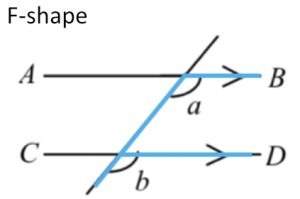 |
If AB // CD, then a = b
corr. ∠s, AB // CD |
If a = b, then AB // CD
corr. ∠s equal |
 |
If AB //CD, then a = b
alt. ∠s, AB // CD |
If a = b, then AB //CD
alt. ∠s equal |
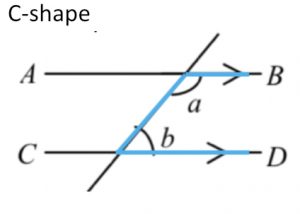 |
If AB // CD,
then a + b = 180° int. ∠s, AB // CD |
If a + b = 180°, then AB // CD
int. ∠s supp. |
| Angles of convex polygon | |
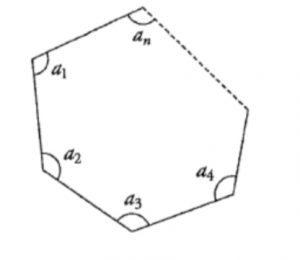 |
a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + … + a_n = (n − 2) × 180°
∠ sum of polygon → Regular 正多邊形 Each interior angle = \frac{(n − 2) × 180°}{n} |
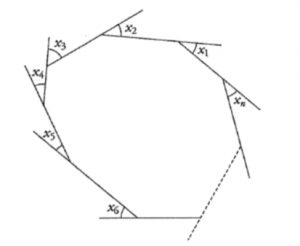 |
x_1 + x_2 + x_3 + … + x_n = 360°
sum of ext. ∠s of polygon → Regular 正多邊形 Each exterior angle = \frac{360º}{n} |
| / Δs | ||
|
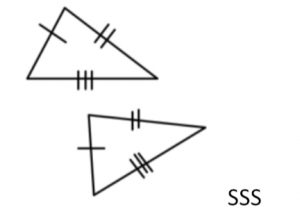
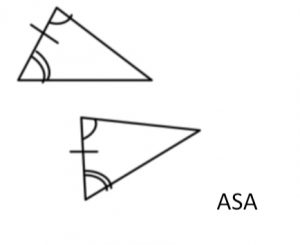
Congruent Triangles (P.S. congruent Δ 係 similar Δ其中一種) |
Similar Triangles | |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
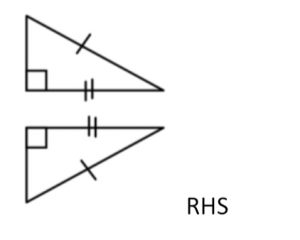 |
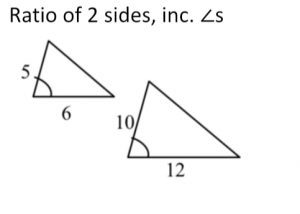 |
|
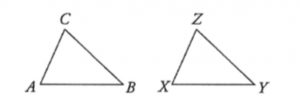
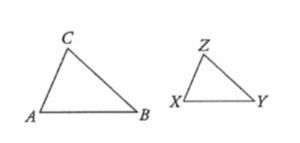
If ΔABC ≅ΔXYZ, then ∠A = ∠X, ∠B = ∠Y, ∠C = ∠Z (corr. ∠s, ≅Δs) AB = XY, BC = YZ, CA = ZX (corr. sides, ≅Δs)
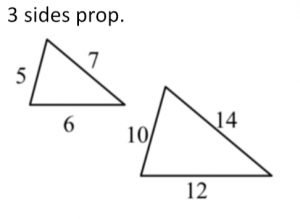
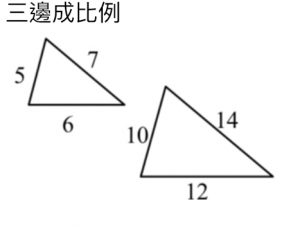
If ΔABC ~ ΔXYZ, then ∠A = ∠X, ∠B = ∠Y, ∠C = ∠Z (corr. ∠s, ≅Δs) \frac{AB}{XY} = \frac{BC}{YZ} = \frac{CA}{ZX} (corr. sides, ~Δs) |
||
| Properties of quadrilateral | ||
| Properties | Prove | |
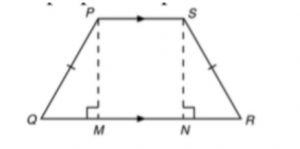 |
∠P + ∠Q = 180°
∠R + ∠S = 180º Prop. of trapezium |
|
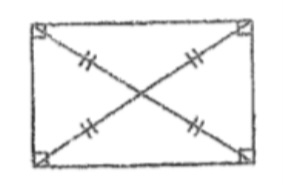 |
90º
+ all prop. of //gram |
|
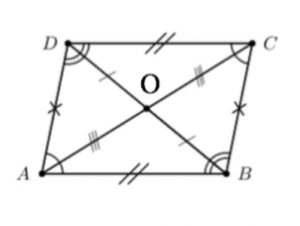 |
AD = BC & AB = DC
∠A = ∠C & ∠B = ∠D AO = CO & BO = DO AD = BC & AD // BC prop. of //gram |
opp. sides equal
opp. ∠s equal diags. bisect each other 2 sides equal and // |
 |
diagonals are ⊥
4 sides equal Interiors are bisected by diagonals + all prop. of //gram Properties of rhombus |
|
→ Right-angled triangle
🌟見到直角唔係畢氏定理就係sin/cos/tan
sin θ = \frac{opp.對}{hyp.斜} = \frac{a}{c}
cos θ = \frac{adj.鄰}{hyp.斜} = \frac{b}{c}
tan θ = \frac{opp.對}{adj.鄰} = \frac{a}{b}
a^2 + b^2 = c^2 (pyth. Them.)
If a^2 + b^2 = c^2, then ∠C = 90º (Converse of Pyth. Thm.)
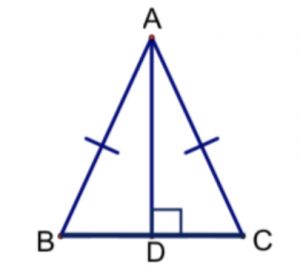
→ Isosceles triangle
If AB = AC, then ∠ABC = ∠ACB (base ∠s, isos. Δ)
If ∠ABC = ∠ACB, then AB = AC (sides opp. equal ∠s)
If ΔABC is an isos. Δ,
then AD ⊥ BC & BD = DC & ∠BAD = ∠CAD (prop. of isos. Δ)
→ Equilateral Triangle
If AB = BC = CA, then ∠A, ∠B, ∠C = 60º, vice versa (prop. of equil. Δ)
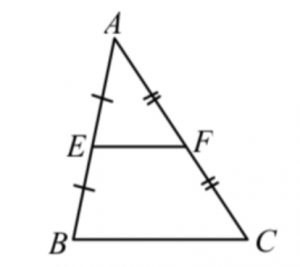
→ Mid-point theorem and Intercept Theorem
If AE = EB and AF = FC, then EF // BC & EF = \frac{1}{2}BC (Mid-pt. theorem)
If AE = EB and EF // BC, then AF = FC (intercept theorem)
If AC = CE and AB // CD // EF, then BD = DF (intercept theorem)
→ Triangle inequality
a + b > c
b + c > a
c + a > b
→ Sine formula (2邊2角):
\frac{a}{sinA} = \frac{b}{simB} = \frac{c}{sinC}
→ Consine formula (3邊1角):
c^2 = a^2 + b^2 − 2abcosC
→ Center formula
 |
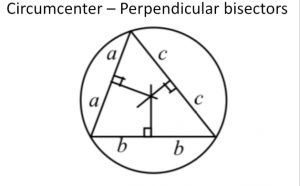 |
 |
 |
→ Symmetry
| Solid | Plane of reflection | Axis of rotation |
| Cube 立方體 | 9 | 13 |
| Tetrahedron 四面體 | 6 | 7 |
| Regular octahedron 正八面體 | 9 | 13 |
Axis of symmetry of n-sided regular polygon = n
Order of rotational symmetry of n-sided regular polygon = n
Number of diagonals of n-sided polygon = \frac{n(n − 3)}{2}
演繹幾何定理
| Angles | 特性 |
 |
a + b = 180°
直線上的鄰角 |
 |
a + b + c = 360°
同頂角 |
 |
a = b
對頂角 |
 |
a + b + c = 180º
Δ內角和 |
 |
a + b = c_1
Δ外角 *快捷版,可不記 |
| Properties | Prove | |
| 平行線
***見到F/Z/C shape先好用 |
||
 |
If AB // CD, then a = b
同位角,AB // CD |
If a = b, then AB//CD
同位角相等 |
 |
If AB // CD, then a = b
錯角,AB // CD |
If a = b, then AB // CD
錯角相等 |
 |
If AB // CD, then a + b = 180°
同旁內角,AB //CD |
If a + b = 180º, then AB // CD
同旁內角互補 |
| 凸多邊形的角 | |
 |
a_1 + a_2 + a_3 + … + a_n = (n − 2) × 180°
多邊形的內角和 → Regular 正多邊形 每隻內角 = \frac{(n − 2) × 180°}{n}
|
 |
x_1 + x_2 + x_3 + … + x_n = 360°
多邊形的外角和 → Regular 正多邊形 每隻外角 = \frac{360°}{n} |
| / Δs | ||
| 全等三角形
(P.S. 全等三角形 係 相似三角形 其中一種) |
相似三角形 | |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|

If ΔABC ≅ ΔXYZ, then ∠A = ∠X, ∠B = ∠Y, ∠C = ∠Z (全等三角形對應角) \frac{AB}{XY} = \frac{BC}{YZ} = \frac{CA}{ZX} (相似三角形對應邊) |
||
| 四邊形的特性 | ||
| 特性 | 證明 | |
 |
∠P + ∠Q = 180°
∠R + ∠S = 180º 梯形性質 |
|
 |
90º
+ 所有平行四邊形性質 |
|
 |
AD = BC & AB = DC
∠A = ∠C & ∠B = ∠D AO = CO & BO = DO AD = BC & AD // BC 平行四邊形性質 |
對邊相等
對角相等 對角線互相平分 一組對邊相等且平行 |
 |
對角線互相垂直
4 邊相等 對角線平分頂角 + 所有平行四邊形性質 菱形性質 |
|
→ 直角三角形
🌟 見到直角唔係畢氏定理就係 sin/cos/tan
sin θ = \frac{對}{斜} = \frac{a}{c}
cos θ = \frac{鄰}{斜} = \frac{b}{c}
tan θ = \frac{對}{鄰} = \frac{a}{b}
a^2 + b^2 = c^2
If a^2 + b^2 = c^2, then ∠C = 90º(畢氏定理逆定理)
→ 等腰三角形
If AB = AC, then ∠ABC = ∠ACB(等腰Δ底角)
If ∠ABC = ∠ACB, then AB = AC(等角對邊相等)
If ΔABC is an isos. Δ, then AD ⊥ BC & BD = DC & ∠BAD = ∠CAD(等腰Δ性質)
→ 等邊三角形
If AB = BC = CA, then ∠A, ∠B, ∠C = 60º, vice versa(等邊Δ性質)
→ 中點定理及截線定理
If AE = EB and AF = FC, then EF // BC & EF = \frac{1}{2}BC(中點定理)
If AE = EB and EF // BC, then AF = FC(截線定理)
If AC = CE and AB // CD // EF, then BD = DF(截線定理)
→ 三角不等式
a + b > c
b + c > a
c + a > b
→ 正弦公式(2邊2角)
\frac{a}{sin A} = \frac{b}{sin B} = \frac{c}{sin C}
→ 餘弦公式(3邊1角)
c^2 = a^2 + b^2 − 2ab cos C
→ 三角形的中心
 |
 |
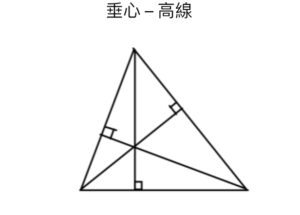 |
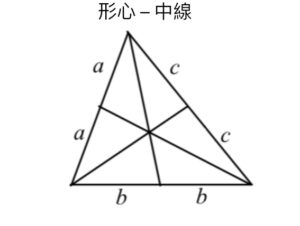 |
→ 對稱
| 立體 No | 反射平面 | 旋轉軸 |
| 立方體 | 9 | 13 |
| 四面體 | 6 | 7 |
| 正八面體 | 9 | 13 |
正n邊形的對稱數 = n
正n邊形的旋轉折式數目 = n
正n邊形的對角線 = \frac{n(n−3)}{2}
適用題目:
DSE 2023 P1 Q8
DSE 2023 P2 Q19
DSE 2023 P2 Q21
DSE 2023 P2 Q23
DSE 2023 P2 Q38
DSE 2023 P2 Q40
Deductive Geometry 演繹幾何定理課程
- Quadratic equations in one unknown 一元二次方程
- Logarithm 對數公式
- Variations 變分
- Polynomials 多項式
- Complex Number 複數
- Laws of integral indices formula 整數指數律公式
- Percentage 百分比公式
- Estimation and Error Formula 誤差公式
- Rate and Ratio Formula 率和比
- Identities 恆等式
- Deductive Geometry 演繹幾何定理
- Mensuration Formula 求積法公式
- Equation of Straight Lines 直線方程
- Quadratic equations in one unknown 一元二次方程
- Logarithm 對數公式
- Variations 變分
- Polynomials 多項式
- Complex Number 複數
- Laws of integral indices formula 整數指數律公式
- Percentage 百分比公式
- Estimation and Error Formula 誤差公式
- Rate and Ratio Formula 率和比
- Identities 恆等式
- Deductive Geometry 演繹幾何定理
- Mensuration Formula 求積法公式
- Equation of Straight Lines 直線方程